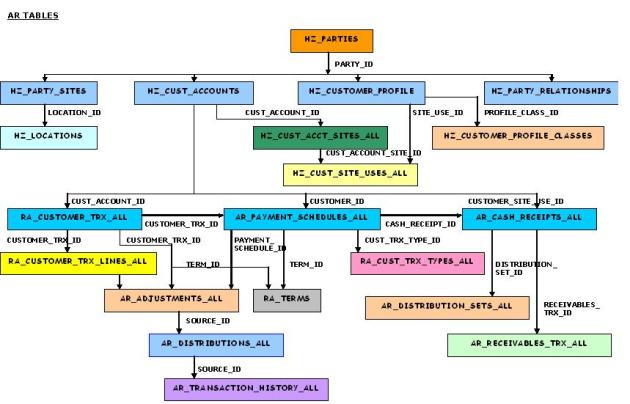
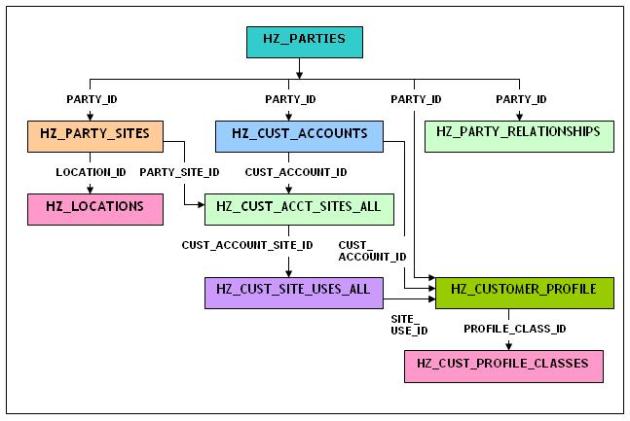
Few Important AP Tables
AP_SUPPLIERS:
- This table replaces the old PO_VENDORS table.
- It stores information about your supplier level attributes.
- Each row includes the purchasing, receiving, invoice, tax, classification, and general information.
- Oracle Purchasing uses this information to determine active suppliers.
- The supplier name, legal identifiers of the supplier will be stored in TCA and a reference to the party created in TCA will be stored in AP_SUPPLIERS.PARTY_ID, to link the party record in TCA.
AP_SUPPLIER_SITES_ALL:
- This table replaces the old PO_VENDOR_SITES_ALL table.
- It stores information about your supplier site level attributes.
- There is a row for unique combination of supplier address, operating unit and the business relationship that you have with the supplier.
- The supplier address information is not maintained in this table and is maintained in TCA. The reference to the internal identifier of address in TCA will be stored in AP_SUPPLIER_SITES_ALL.LOCATION_ID, to link the address record in TCA.
- Each row includes the supplier reference, purchasing, invoice, and general information.
AP_INVOICES_ALL:
- It contains records for invoices you enter.
- There is one row for each invoice you enter.
- An invoice can have one or more invoice distribution lines and can have one or more scheduled payments.
AP_INVOICE_LINES_ALL:
- It contains records for invoice lines entered manually, generated automatically or imported from the Open Interface.
- An invoice can have one or more invoice lines.
- An invoice line represents goods (direct or indirect materials), service(s), and/or associated tax/freight/miscellaneous charges invoiced from a supplier.
- An invoice line should contain all the attributes that are present on the physical or electronic invoice presented by the supplier.
AP_INVOICE_DISTRIBUTIONS_ALL:
- It holds the distribution information that is manually entered or system-generated.
- There is one row for each invoice distribution and a distribution must be associated with an invoice.
- An invoice can have multiple distributions.
AP_INVOICE_PAYMENTS_ALL:
- It contains records of invoice payments that you made to suppliers.
- There is one row for each payment you make for each invoice and there is one payment and one invoice for each payment in this table.
- Oracle Payables application updates this table when you confirm an automatic payment batch, enter a manual payment, or process a Quick payment.
- When you void a payment, your Oracle Payables inserts an additional payment line that is the negative of the original payment line.
AP_PAYMENT_SCHEDULES_ALL:
- This table stores information about scheduled payment information on invoices.
AP_PAYMENT_HISTORY_ALL:
- It stores the clearing/unclearing history for payments.
- It also stores the maturity history for future dated payments.
- The table contains a row for each future dated payment, once the future dated payment matures, i.e. becomes negotiable.
- Any time a payment is cleared or uncleared, a row is inserted into this table for the payment.
AP_BATCHES_ALL:
- It contains summary information about invoices you enter in batches if you enable the Batch Control Payables option.
- There is one row for each batch of invoices you enter.
- If you enable Batch Control, each invoice must correspond to a record in this table.
- Your Oracle Payables application uses this information to group together invoices that one person entered in a batch.
AP_CHECKS_ALL:
- It stores information about payments issued to suppliers or refunds received from suppliers.
- There is one row for each payment you issue to a supplier or refund received from a supplier.
- Oracle Payables application uses this information to record payments you make to suppliers or refunds you receive from suppliers.
- Oracle Payables application stores the supplier name and bank account name for auditing purposes, in case either one is changed after you create the payment. Oracle Payables application also stores address information for all payments.
AP_HOLDS_ALL:
- It contains information about holds that you or your Oracle Payables application place on an invoice.
- For non-matching holds, there is one row for each hold placed on an invoice. For matching holds, there is one row for each hold placed on an invoice-shipment match.
- An invoice may have one or more corresponding rows in this table.
- Your Oracle Payables application does not pay invoices that have one or more unreleased holds recorded in this table.
AP_BANK_ACCOUNTS_ALL:
- It contains information about your bank accounts.
- There is one row for each bank account you define and each bank account must be affiliated with one bank branch.
AP_BANK_ACCOUNT_USES_ALL:
- It stores information for the internal and external bank accounts you define in Oracle Payables and Oracle Receivables applications.
AP_CARDS_ALL:
- It stores information about the corporate credit cards issued to your employees by your corporate credit card providers.
AP_TRIAL_BALANCE:
- It contains denormalized information about invoices and payments posted to the accrual set of books.