AR (Accounts Receivable)
Receivables overview:
Accounts receivable is an asset account in the general ledger that documents money owed to a business by customers who have purchases goods or services on credit.
Receivables Workbenches:
Oracle Receivables provides four integrated workbenches that you can use to perform most of your day–to–day Accounts Receivable operations. You can use the
1- Receipts Workbench to perform most of your receipt–related tasks.
2- Transactions Workbench to process your invoices, debit memos, credit memos, on–account credits, charge backs, and adjustments.
3- Collections Workbench lets you review customer accounts and perform collection activities such as recording customer calls and printing dunning letters.
4- Bills Receivable Workbench lets you create, update, remit, and manage your bills receivable.
AR Required Steps:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1- Receivable Activities:
Receivables->Setup->Receipts->Receivable Activities
Define receivables activities to default accounting information for your miscellaneous receipt, finance charge, chargeback, and adjustment transactions. The activities you define appear as list of values choices in the Receipt and Adjustment windows.
7- Auto Accounting
Receivables->Setup->Transactions->Auto Accounting:
Define AutoAccounting to specify how you want Receivables to determine the general ledger accounts for transactions that you enter manually or import using AutoInvoice. Receivables creates default accounts for revenue, receivable, freight, tax, unearned revenue, unbilled receivable, finance charges, and AutoInvoice clearing (suspense) accounts using this information.
When you enter transactions in Receivables, you can override the default general ledger accounts that AutoAccounting creates.
You can control the value that AutoAccounting assigns to each segment of your Accounting Flexfield, such as Company, Division, or Account.
You must define AutoAccounting before you can enter transactions in Receivables
11- System Options
12: Adjustment Approval Limits
Receivables->Setup->Auto Invoice-> Approval Limits
You can define adjustment approval limits for each of your users. Receivables enforces these limits when you either create or approve invoice, debit memo, and chargeback adjustments in the Adjustments, Submit AutoAdjustments, and Approve Adjustments windows.
When you enter an adjustment that is outside your approval limit range, Receivables assigns a pending adjustment status until someone with the appropriate approval limits approves or rejects the adjustment. You must specify both lower and upper approval limits for each of your users
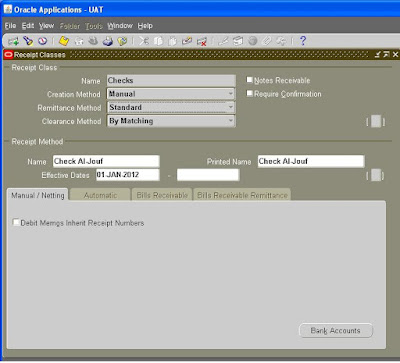
13: Payment Method
Receivables->Setup->Receipts->Receipt Classes
Receivables uses payment methods to account for your receipt entries and applications. Payment methods also determine a customer's remittance bank information.
Prerequisites
 Define receipt classes
Define receipt classes
 Define banks
Define banks
Accounts receivable is an asset account in the general ledger that documents money owed to a business by customers who have purchases goods or services on credit.
Receivables Workbenches:
Oracle Receivables provides four integrated workbenches that you can use to perform most of your day–to–day Accounts Receivable operations. You can use the
1- Receipts Workbench to perform most of your receipt–related tasks.
2- Transactions Workbench to process your invoices, debit memos, credit memos, on–account credits, charge backs, and adjustments.
3- Collections Workbench lets you review customer accounts and perform collection activities such as recording customer calls and printing dunning letters.
4- Bills Receivable Workbench lets you create, update, remit, and manage your bills receivable.
AR Required Steps:
| Step 1: | Define Your Set of Books (Required) |
| Step 2: | Decide How to Use the Account Generator (Required) |
| Step 3: | Define Your System Item Flexfield Structure (Required) |
| Step 4: | Define Your Organizations (Required) |
| Step 5: | Define Your Sales Tax Location Flexfield Structure (Required with Defaults) |
| Step 6: | Define Your System Options (Required) |
| Step 7: | Define Your Payment Terms (Required with Defaults) |
| Step 8: | Open Your Accounting Periods (Required) |
| Step 9: | Define Your Auto Accounting (Required) |
| Step 10: | Define Your Transaction Types (Required with Defaults) |
| Step 11: | Define Your Transaction Sources (Required) |
| Step 12: | Define Your Collectors (Required with Defaults) |
| Step 13: | Define Your Adjustment Approval Limits (Required) |
| Step 14: | Define Your Remittance Banks (Required) |
| Step 15: | Define Your Receivables Activities (Required) |
| Step 16: | Define Your Receipt Classes (Required) |
| Step 17: | Define Your Payment Methods (Required) |
| Step 18: | Define Your Receipt Sources (Required) |
| Step 19: | Define Your Aging Buckets (Required with Defaults) |
| Step 20: | Define Your Salespeople (Required with Defaults) |
| Step 21: | Define Your Profile Options (Required) |
| Step 22: | Define Your Tax Codes and Rates (Required) |
| Step 23: | Define Your Customer Profile Classes (Required with Defaults) |
| Step 24: | Define Your Customers (Required) |
| Step 25: | Define Your Remit-To Addresses (Required) |
| Step 26: | Define Your Units of Measure (Required with Defaults) |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1- Receivable Activities:
Receivables->Setup->Receipts->Receivable Activities
Define receivables activities to default accounting information for your miscellaneous receipt, finance charge, chargeback, and adjustment transactions. The activities you define appear as list of values choices in the Receipt and Adjustment windows.
2- Receipt Class:
Receivables->Setup->Receipts->Receipt Classes
Define receipt classes to determine the required processing steps for receipts to which you assign payment methods with this class.
3- Receipt Source:
Receivables->Setup->Receipts->Receipt Sources
Define receipt batch sources to provide default values for the receipt class, payment method, and remittance bank account fields for receipts you add to a receipt batch. You can accept these default values or enter new ones. Receipt batch sources can use either automatic or manual batch numbering.
4- Customer Profile Class:
Receivables->Customers->Profile Classes
You must define customer profile classes to categorize your customers based on credit, payment terms, statement cycles, automatic receipt, finance charge, dunning, and invoicing information. When you initially set up your customers, you assign each customer to a profile class. To customize the profile class for a specific customer, use the Customer Profile Classes window. Receivables provides the predefined customer profile class 'DEFAULT'.
5- Transaction Type:
Receivables->Setup->Transactions->Types
Define the transaction types that you assign to your invoices, debit memos, commitments, chargebacks, credit memos, and on-account credits. Receivables uses transaction types to default payment term, account, tax, freight, creation sign, posting, and receivables information. Receivables provides two predefined transaction types: 'Invoice' and 'Credit Memo'.
6- Transaction Sources:
Receivables->Setup->Transactions->Sources
Define the transaction sources that you will assign to your invoices, debit memos, commitments, credit memos, and on-account credits. Receivables uses transaction sources to control your transaction and transaction batch numbering, to specify your default transaction type, and to select validation options for imported transactions. Before you can define a transaction source for your invoices, you must define transaction sources for your credit memos. Receivables provides the following predefined transaction sources: 'MANUAL-OTHER', 'DM Reversal,' and 'Chargeback'.
Receivables->Setup->Transactions->Auto Accounting:
Define AutoAccounting to specify how you want Receivables to determine the general ledger accounts for transactions that you enter manually or import using AutoInvoice. Receivables creates default accounts for revenue, receivable, freight, tax, unearned revenue, unbilled receivable, finance charges, and AutoInvoice clearing (suspense) accounts using this information.
When you enter transactions in Receivables, you can override the default general ledger accounts that AutoAccounting creates.
You can control the value that AutoAccounting assigns to each segment of your Accounting Flexfield, such as Company, Division, or Account.
You must define AutoAccounting before you can enter transactions in Receivables
8- Collectors
Receivables->Setup->Collections->Collectors
Receivables lets you define collectors and assign them to a profile class or to a customer's credit profile class. When you assign a collector a to profile class, that collector becomes the collector for customers to whom you assign that profile class. You can modify collector assignments for your customers in the Customers window and for your profile classes in the Customer Profile Classes window.
9- Remit to Address
Receivables->Setup->Print->Remit to Addresses
Define remit-to addresses to let your customers know where to send payment for their invoices. Receivables uses the addresses that you define in the Remit To Addresses window to provide default remit-to information when you enter transactions.
If you use AutoInvoice but have not defined a remit-to address for a location, AutoInvoice will reject all invoices for which it could not determine a remit-to address. However, if you do not wish to set up a remit-to address for each location, you can set up one remit-to address with a default assignment
10- Sales Persons
Receivables ->Setup-> Auto Invoice-> Sales Persons
Define the salespeople you assign to your invoices, debit memos, and commitments to allocate sales credits. If you do not want to assign sales credits to a transaction, you can enter 'No Sales Credit'.
Receivables ->Setup-> System -> System Options
Receivables->Setup->Auto Invoice-> Approval Limits
You can define adjustment approval limits for each of your users. Receivables enforces these limits when you either create or approve invoice, debit memo, and chargeback adjustments in the Adjustments, Submit AutoAdjustments, and Approve Adjustments windows.
When you enter an adjustment that is outside your approval limit range, Receivables assigns a pending adjustment status until someone with the appropriate approval limits approves or rejects the adjustment. You must specify both lower and upper approval limits for each of your users
Receivables->Setup->Receipts->Receipt Classes
Receivables uses payment methods to account for your receipt entries and applications. Payment methods also determine a customer's remittance bank information.
Prerequisites












Hey I’m Martin Reed,if you are ready to get a loan contact.Mr Benjamin via email: lfdsloans@lemeridianfds.com,WhatsApp:+1 989-394-3740 I’m giving credit to Le_Meridian Funding Service .They grant me the sum 2,000,000.00 Euro. within 5 working days. Le_Meridian Funding Service is a group investors into pure loan and debt financing at the returns of 1.9% to pay off your bills or buy a home Or Increase your Business. please I advise everyone out there who are in need of loan and can be reliable, trusted and capable of repaying back at the due time of funds.
ReplyDeleteAccounts receivable or AR are the unpaid bills or invoices a company has sent to its customers in the simplest sense.
ReplyDelete