1 Overview of Oracle Alerts
2 Defining Alerts
3 Type of Alerts
4 Check the Alerts
Overview of Oracle Alerts:
· Keep you informed of critical activity in your database
· Deliver key information from your applications, in the format you choose
· Provide you with regular reports on your database information
· Automate system maintenance, and routine online tasks
Oracle Alert is your complete exception control solution.
Oracle Alert facilitates the flow of information within your organization by letting you create entities called alerts to monitor your business information and to notify you of the information you want. You can define one of two types of alerts: an event alert or a periodic alert.
An event alert immediately notifies you of activity in your database as it occurs. When you create an event alert, you specify the following:
· A database event that you want to monitor, that is, an insert and/or an update to a specific database table.
· A SQL Select statement that retrieves specific database information as a result of the database event.
· Actions that you want Oracle Alert to perform as a result of the database event. An action can entail sending someone an electronic mail message, running a concurrent program, running an operating script, or running a SQL statement script. You include all the actions you want Oracle Alert to perform, in an action set.
A periodic alert, on the other hand, checks the database for information according to a schedule you define. When you create a periodic alert, you specify the following:
· A SQL Select statement that retrieves specific database information.
· The frequency that you want the periodic alert to run the SQL statement.
· Actions that you want Oracle Alert to perform once it runs the SQL statement. An action can entail sending the retrieved information to someone in an electronic mail message, running a concurrent program, running an operating script, or running a
· SQL statement script.
Navigator: Alert Vision Manager USA
To define Alerts

Periodic alerts periodically report key information according to a schedule you define.
To define a periodic alert:
1. Navigate to the Alerts form.
2. Enter the name of the application that owns the alert in the
Application field. This application must reside in the same Oracle database as Oracle Alert.
3. Name the alert (up to 50 characters), and give it a meaningful description (up to 240 characters).
4.Enter a name for the alert that is unique within the application. Use an initial character other than a pound sign (#), a colon (:), or a percentage sign (%).
1. Select a frequency for your periodic alert. You can choose from nine frequency options:
2.
Frequency :
On Demand :-We have to run the alert to fire.
Enter which Application u want to specify alerts, name of the alert,
Click whether its periodic or Event
On Day of Month: It will fire last day of every month.
It will start from 12 AM up to 11 AM morning and each 2 hours interval the alert will fire once.
Exa: 12AM, 2 AM, 4 AM … … … … 8am, 10am.

On Day of Week : Same as On day of Month.
Every N Calendar day: It will fire in each two days.
Every N Business Day: It will fire once in each three business day.(It will not count the holidays)
Every Day: It will fire daily
Every Other Day : It will fire in a alternative day.
Every Business Day: It will fire every day except holiday.
Every Other Business Day: It will fire in an alternative business (working) day.
i.e It will not consider holidays
Import : We can import the files(which contain the query) if the query size is big, if it exceed the memory.



After writing the Query in Select Statement area click on Verify to verify the query and

After Click on Verify Button the following message will come.
Click on OK and Save
Then click on Run to execute the query.
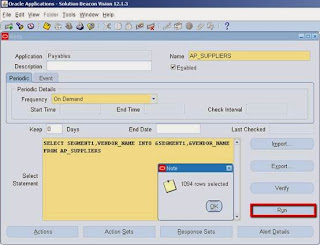
Click on Run button , the following screen will come. And click on OK.
2 . Click on Actions Button and enter the Action information like following screen
Details Action perform once for each exception found,
Summary Action perform once for all exception found
No exception performs when no exception was found.

2.click on Action Details and enter the value and save.
Concurrent Program : Used to execute the Concurrent program.
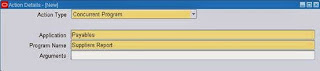
Message : Used to send the message via mail.
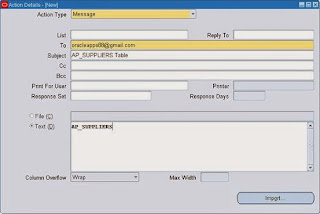
Operating System Script: Used to run the OS Script.
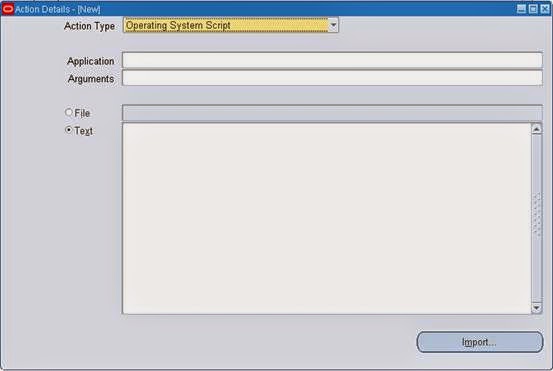
SQL Statement Script : Used to run the SQL statement Script.
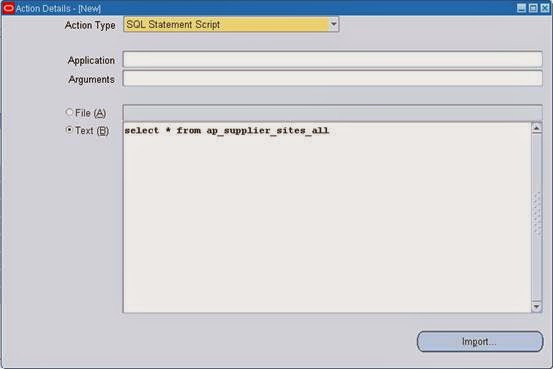
3. Click on Action Sets button from Alert window
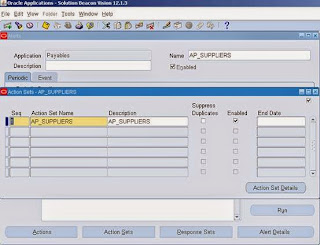
Then click on Action Set Details
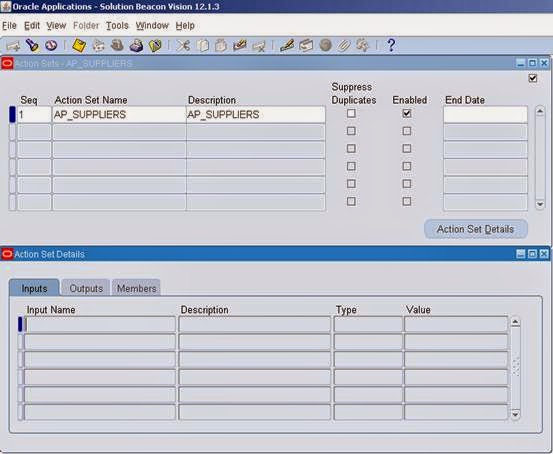
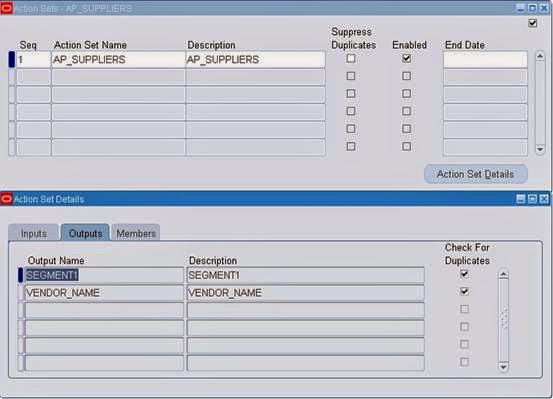
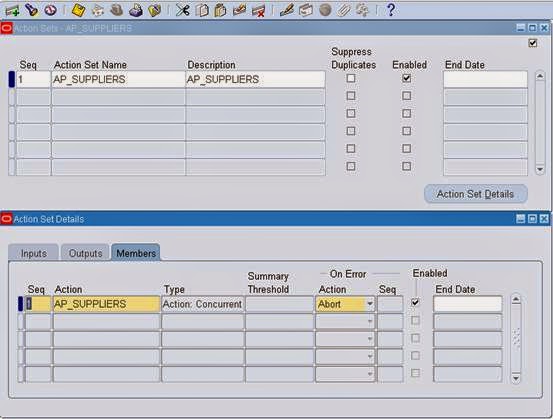
4. Then click on Alert Details from the Alert window and enter the value and save.
Creating an Event Alert
To create an event alert, you perform the following tasks in the order listed:
• Define the database events that will trigger your alert
• Specify the details for your alert
• Define actions for your alert
• Create action sets containing the actions you want your alert to perform
This section focuses on the first task of defining the database events that trigger your event alert and divides the task into smaller sub–tasks.
To define an event alert:
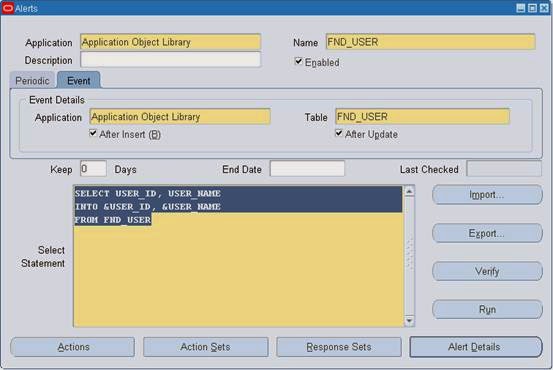
1. Navigate to the Alerts form.
2. In the Application field, use the list of values to choose the name of the application that owns the alert. This application must reside in the same Oracle database as Oracle Alert.
3. Name the alert (up to 50 characters), and give it a meaningful description (up to 240 characters).
Enter a name for the alert that is unique within the application. Use an initial character other than a pound sign (#), a colon (:), or a percentage sign (%).
4. In the Type field, choose Event.
5. Check Enabled to enable your event alert.
To specify the alert details for an event or periodic alert:
1. With your alert definition displayed in the Alerts form, choose Alert Details. The Alert Details window that appears contains three tabbed regions: Installations, Inputs, and Outputs.
2. In the Inputs tabbed region, Oracle Alert automatically displays the inputs used in your Select statement, unless they are the implicit
inputs: :ROWID, :MAILID, :ORG_ID and :DATE_LAST_CHECKED.
The values of the implicit inputs are as follows:
• ROWID—Contains the ID number of the row where the insert or update that triggers an event alert occurs.
• MAILID—Contains the email username of the person who enters an insert or update that triggers an event alert.
• ORG_ID—Contains the organization ID that is selected when the alert runs.
• DATE_LAST_CHECKED—Contains the date and time that the alert was most recently checked.
3. You can optionally add a description for each input, but you must specify the data type (either character, number, or date) for the input, because Oracle Alert uses the data type to validate the default values for inputs you enter in the Default Values field and in the Action Set Inputs tabbed region of the Action Sets block.
4. Enter a default value for your input. You can enter up to 240 characters. This value automatically becomes the default value for your input in each action set you define.
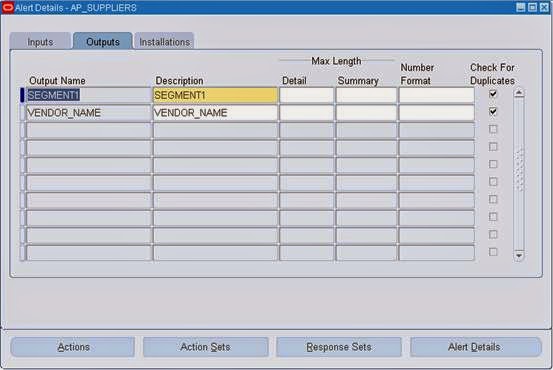
5. In the Outputs tabbed region, Oracle Alert automatically displays the outputs used in your alert Select statement without the ampersand (&) and any numbering format. You can add meaningful descriptions for the outputs.
6. You can specify the maximum number of output characters you want to display in your detail or summary message actions. See: Formatting Summary Message Actions:
7. If your output value is numeric, enter the SQL*Plus format mask in the Number Format field.
8. You can also check the Check for Duplicates check box to customize the combination of outputs you want to verify as a possible duplicate exception each time the alert is checked. A duplicate exception is an exception that existed in your database during previous alert checks. You can define Oracle Alert to perform certain actions based on the presence of these duplicate exceptions.
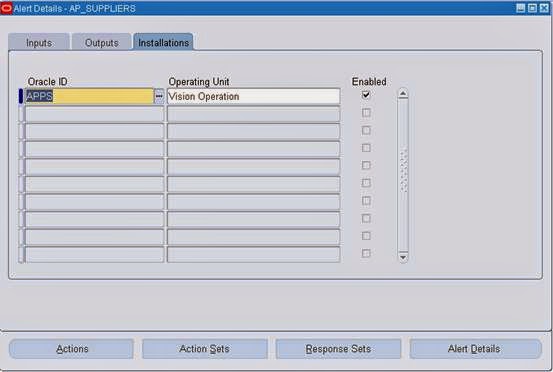
9. In the Installations tabbed region, specify an Oracle ID if you want Oracle Alert to check your alert against that specific Oracle ID. You can select only those Oracle IDs that are associated with the application that owns your alert.
If you do not specify an Oracle ID in this region, Oracle Alert checks your alert against all installations in your database of the application that owns your alert.
10. If you have multiple organizations defined in your Oracle Applications schema, you must specify the organization you want the alert to run against in the Operating Unit field.
Click Action details,
In Action details Navigator
They are four types of Actions
Concurrent Program : Used to execute the Concurrent program.
Message : Used to send the message via mail.
Operating System Script: Used to run the OS Script.
SQL Statement Script : Used to run the SQL statement Script.
(N) Request>Check
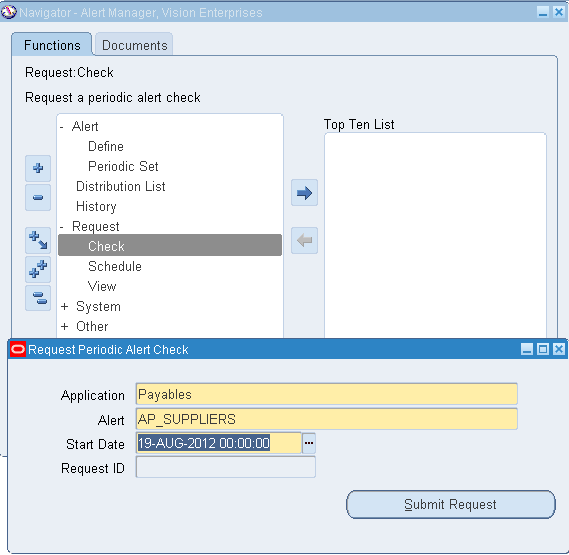
Then View> Request >Find from Alert Manager responsibility.
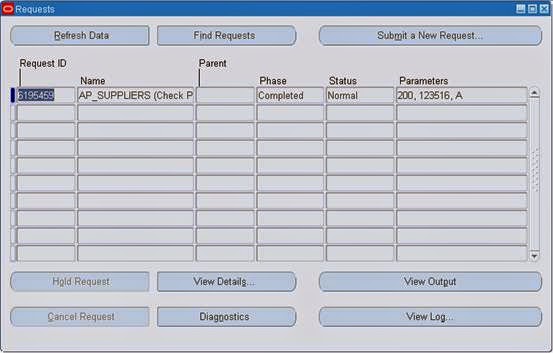
After completed Normal check the mail.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Query to find Custom Oracle Alert
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SELECT alr.application_id,
alr.alert_id,
alr.alert_name,
alr.start_date_active,
alr.description,
alr.sql_statement_text
FROM alr.alr_alerts alr
WHERE 1=1
AND alr.created_by <> 1 -- show only custom alerts
AND alr.enabled_flag = 'Y'; -- show only enabled alerts
2 Defining Alerts
3 Type of Alerts
4 Check the Alerts
Overview of Oracle Alerts:
· Keep you informed of critical activity in your database
· Deliver key information from your applications, in the format you choose
· Provide you with regular reports on your database information
· Automate system maintenance, and routine online tasks
Overview:
Oracle Alert is your complete exception control solution.
Oracle Alert facilitates the flow of information within your organization by letting you create entities called alerts to monitor your business information and to notify you of the information you want. You can define one of two types of alerts: an event alert or a periodic alert.
An event alert immediately notifies you of activity in your database as it occurs. When you create an event alert, you specify the following:
· A database event that you want to monitor, that is, an insert and/or an update to a specific database table.
· A SQL Select statement that retrieves specific database information as a result of the database event.
· Actions that you want Oracle Alert to perform as a result of the database event. An action can entail sending someone an electronic mail message, running a concurrent program, running an operating script, or running a SQL statement script. You include all the actions you want Oracle Alert to perform, in an action set.
A periodic alert, on the other hand, checks the database for information according to a schedule you define. When you create a periodic alert, you specify the following:
· A SQL Select statement that retrieves specific database information.
· The frequency that you want the periodic alert to run the SQL statement.
· Actions that you want Oracle Alert to perform once it runs the SQL statement. An action can entail sending the retrieved information to someone in an electronic mail message, running a concurrent program, running an operating script, or running a
· SQL statement script.
Defining Alerts:
Navigator: Alert Vision Manager USA
To define Alerts

Types of Alerts:
1. Periodic Alerts
Periodic alerts periodically report key information according to a schedule you define.
To define a periodic alert:
1. Navigate to the Alerts form.
2. Enter the name of the application that owns the alert in the
Application field. This application must reside in the same Oracle database as Oracle Alert.
3. Name the alert (up to 50 characters), and give it a meaningful description (up to 240 characters).
4.Enter a name for the alert that is unique within the application. Use an initial character other than a pound sign (#), a colon (:), or a percentage sign (%).
1. Select a frequency for your periodic alert. You can choose from nine frequency options:
2.
Frequency :
On Demand :-We have to run the alert to fire.
Enter which Application u want to specify alerts, name of the alert,
Click whether its periodic or Event
On Day of Month: It will fire last day of every month.
It will start from 12 AM up to 11 AM morning and each 2 hours interval the alert will fire once.
Exa: 12AM, 2 AM, 4 AM … … … … 8am, 10am.

On Day of Week : Same as On day of Month.
Every N Calendar day: It will fire in each two days.
Every N Business Day: It will fire once in each three business day.(It will not count the holidays)
Every Day: It will fire daily
Every Other Day : It will fire in a alternative day.
Every Business Day: It will fire every day except holiday.
Every Other Business Day: It will fire in an alternative business (working) day.
i.e It will not consider holidays
Import : We can import the files(which contain the query) if the query size is big, if it exceed the memory.



After writing the Query in Select Statement area click on Verify to verify the query and

After Click on Verify Button the following message will come.
Click on OK and Save
Then click on Run to execute the query.

Click on Run button , the following screen will come. And click on OK.
2 . Click on Actions Button and enter the Action information like following screen
Details Action perform once for each exception found,
Summary Action perform once for all exception found
No exception performs when no exception was found.

2.click on Action Details and enter the value and save.
Concurrent Program : Used to execute the Concurrent program.

Message : Used to send the message via mail.

Operating System Script: Used to run the OS Script.

SQL Statement Script : Used to run the SQL statement Script.

3. Click on Action Sets button from Alert window

Then click on Action Set Details



4. Then click on Alert Details from the Alert window and enter the value and save.


Event Alerts:
Creating an Event Alert
To create an event alert, you perform the following tasks in the order listed:
• Define the database events that will trigger your alert
• Specify the details for your alert
• Define actions for your alert
• Create action sets containing the actions you want your alert to perform
This section focuses on the first task of defining the database events that trigger your event alert and divides the task into smaller sub–tasks.
To define an event alert:
1. Navigate to the Alerts form.
2. In the Application field, use the list of values to choose the name of the application that owns the alert. This application must reside in the same Oracle database as Oracle Alert.
3. Name the alert (up to 50 characters), and give it a meaningful description (up to 240 characters).
Enter a name for the alert that is unique within the application. Use an initial character other than a pound sign (#), a colon (:), or a percentage sign (%).
4. In the Type field, choose Event.
5. Check Enabled to enable your event alert.

To specify the alert details for an event or periodic alert:
1. With your alert definition displayed in the Alerts form, choose Alert Details. The Alert Details window that appears contains three tabbed regions: Installations, Inputs, and Outputs.
2. In the Inputs tabbed region, Oracle Alert automatically displays the inputs used in your Select statement, unless they are the implicit
inputs: :ROWID, :MAILID, :ORG_ID and :DATE_LAST_CHECKED.
The values of the implicit inputs are as follows:
• ROWID—Contains the ID number of the row where the insert or update that triggers an event alert occurs.
• MAILID—Contains the email username of the person who enters an insert or update that triggers an event alert.
• ORG_ID—Contains the organization ID that is selected when the alert runs.
• DATE_LAST_CHECKED—Contains the date and time that the alert was most recently checked.
3. You can optionally add a description for each input, but you must specify the data type (either character, number, or date) for the input, because Oracle Alert uses the data type to validate the default values for inputs you enter in the Default Values field and in the Action Set Inputs tabbed region of the Action Sets block.
4. Enter a default value for your input. You can enter up to 240 characters. This value automatically becomes the default value for your input in each action set you define.
5. In the Outputs tabbed region, Oracle Alert automatically displays the outputs used in your alert Select statement without the ampersand (&) and any numbering format. You can add meaningful descriptions for the outputs.
6. You can specify the maximum number of output characters you want to display in your detail or summary message actions. See: Formatting Summary Message Actions:
7. If your output value is numeric, enter the SQL*Plus format mask in the Number Format field.
8. You can also check the Check for Duplicates check box to customize the combination of outputs you want to verify as a possible duplicate exception each time the alert is checked. A duplicate exception is an exception that existed in your database during previous alert checks. You can define Oracle Alert to perform certain actions based on the presence of these duplicate exceptions.
9. In the Installations tabbed region, specify an Oracle ID if you want Oracle Alert to check your alert against that specific Oracle ID. You can select only those Oracle IDs that are associated with the application that owns your alert.
If you do not specify an Oracle ID in this region, Oracle Alert checks your alert against all installations in your database of the application that owns your alert.
10. If you have multiple organizations defined in your Oracle Applications schema, you must specify the organization you want the alert to run against in the Operating Unit field.
Click Action details,
In Action details Navigator
They are four types of Actions
Concurrent Program : Used to execute the Concurrent program.
Message : Used to send the message via mail.
Operating System Script: Used to run the OS Script.
SQL Statement Script : Used to run the SQL statement Script.
Check the Alert:
1. Go to Alert Manager(N) Request>Check

Then View> Request >Find from Alert Manager responsibility.

After completed Normal check the mail.
Query to Find Out Oracle Alerts
The following query finds all enabled custom alerts. You can comment out the very last two lines (alr.enabled_flag and alr.created_by) to display all both enabled and disabled alerts.-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Query to find Custom Oracle Alert
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SELECT alr.application_id,
alr.alert_id,
alr.alert_name,
alr.start_date_active,
alr.description,
alr.sql_statement_text
FROM alr.alr_alerts alr
WHERE 1=1
AND alr.created_by <> 1 -- show only custom alerts
AND alr.enabled_flag = 'Y'; -- show only enabled alerts
Oracle Apps Alerts Tables:
| Oracle Apps Alerts Table |
| ALR_ACTION_DATA |
| ALR_ACTION_GROUP_MEMBERS |
| ALR_ACTION_GROUPS |
| ALR_ACTION_HISTORY |
| ALR_ACTION_OUTPUTS |
| ALR_ACTION_SET_CHECKS |
| ALR_ACTION_SET_INPUTS |
| ALR_ACTION_SET_MEMBERS |
| ALR_ACTION_SET_OUTPUTS |
| ALR_ACTION_SETS |
| ALR_ACTIONS |
| ALR_ACTUAL_RESPONSES |
| ALR_ALERT_CHECKS |
| ALR_ALERT_INPUTS |
| ALR_ALERT_INSTALLATIONS |
| ALR_ALERT_OUTPUTS |
| ALR_ALERTS |
| ALR_ALERTS_A |
| ALR_DISTRIBUTION_LISTS |
| ALR_LOOKUPS |
| ALR_MESSAGE_SYSTEMS |
| ALR_ORACLE_MAIL_ACCOUNTS |
| ALR_OUTPUT_HISTORY |
| ALR_PERIODIC_SET_MEMBERS |
| ALR_PERIODIC_SETS |
| ALR_PROFILE_OPTIONS |
| ALR_RESPONSE_ACTION_HISTORY |
| ALR_RESPONSE_ACTIONS |
| ALR_RESPONSE_MESSAGES |
| ALR_RESPONSE_SETS |
| ALR_RESPONSE_VARIABLE_VALUES |
| ALR_RESPONSE_VARIABLES |
| ALR_VALID_RESPONSES |
Oracle Alerts interview questions
What are Oracle Alerts?
Oracle Alerts are used to monitor unusual or critical activity within a designated database. The flexibility of ALERTS allows a database administrator the ability to monitor activities from table space sizing to activities associated with particular applications. Alerts can be created to monitor a process in the database and to notify a specific individual of the status of the process.
2. What are the different types of alerts, Define it?
You can define one of two types of alerts: an event alert or a periodic alert.
Event alert: An event alert immediately notifies you of activity in your database as it occurs.
Periodic alert: A periodic alert, on the other hand, checks the database for information according to a Schedule you define.
3. What are the different business uses of Alerts?
a) Keep you informed of critical activity in your database
b) Deliver key information from your applications, in the format you choose to provide you with regular reports on your database information
c) Automate system maintenance and routine online tasks Information about exception conditions.
4. What can be done with Alerts?
· You can send notifications
· You can send log files as attachments to notifications
· You can call PL/SQL stored procedures.
· You can send approval emails and get the results.
· Print some content dynamically
5. What types of actions can be generated when an Alert is triggered?
When an alert is executed, the alert can send an email message, run a concurrent program, run an operating system script, or run a SQL statement script. Using response processing, Oracle Alerts can solicit a response from a specific individual and perform an action based on the response that it receives.
6. What is On-Demand periodic alert?
It is a periodic alert with frequency as ‘On-Demand’. That means there is no specific period assigned to this alert and you can run this alert at any time you want using Request Periodic Alert Check form.
7. What database events can cause what actions?
An insert and/or an update to a specific database table
8. What actions can you perform in an alert?
An action can entail sending someone an electronic mail message, running a concurrent program, running an operating script, or running a SQL statement script. You include all the actions you want Oracle Alert to perform, in an action set.
9. How event alert works?
When you define an event alert to monitor a table for inserts and/or updates, any insert or update to the table will trigger the event alert. When an insert or update to an event table occurs, Oracle Alert submits to the concurrent manager, a request to run a concurrent program called Check Event Alert. The concurrent manager runs this request according to its priority in the concurrent queue. When the request is run, Check Event Alert executes the alert Select statement. If the Select statement finds exceptions, Check Event Alert performs the actions defined in the enabled action set for the alert. If the Select statement does not find any exceptions, Check Event Alert performs the No Exception actions in the enabled action set for the alert.
10. What do you specify when creating a Periodic Alert?
a. A SQL Select statement that retrieves specific database information
b. The frequency that you want the periodic alert to run the SQL statement
c. Actions that you want Oracle Alert to perform once it runs the SQL statement.
11. Can you define Alert on Oracle Applications Tables?
Yes
12. What is Periodic Set?
You can create a set of periodic alerts that Oracle Alert checks simultaneously. Use the Request Periodic Alert Check window to check the periodic set. Note that each periodic alert you include in a periodic set continues to run according to its individually defined frequency.
13. How alert is different from database triggers?
a) Code can be modified and viewed in a screen
b) Periodic alert is not possible through Database trigger
c) Oracle Alert will also transfer your entire alert definition across databases. You can instantly leverage the work done in one area to all your systems.
d) Customizable Alert Frequency with Oracle Alert, you can choose the frequencyof each periodic alert. You may want to check some alerts every day, some only once a month, still others only when you explicitly request them.
14. What is Action Set?
An action set can include an unlimited number of actions and any combination of actions and action groups for your alert. You can define as many action sets as you want for each alert. Oracle Alert executes the alert Select statement once for each action set you define. During each action set check, Oracle Alert executes each action set member in the sequence you specify.
15. Can you define detailed or summary actions in alert?
Yes, Detail or Summary Actions you can choose to have Oracle Alert perform actions based on a single exception or a combination of exceptions found in your database.
16. What is Distribution List in Oracle Alert?
Distribution lists let you predefine a set of message recipients for use on many actions. If a recipient changes, you need only adjust it in the distribution list, not in the individual message actions.
17. Can you specify History Maintenance?
Alert History Oracle Alert can keep a record of the actions it takes and the exceptions it finds in your database, for as many days as you specify.
18. Can you perform actions when NO exceptions are found?
No Exception Actions : Oracle Alert can perform actions if it finds no exceptions in your database, same as alert actions.
19. What are the Action Levels for your alert actions?
There are three types of level for your action: Detail, Summary and No Exception.
During an alert check, a detail action performs once for each individual exception found, a summary action performs once for all exceptions found, and a no exception action performs when no exceptions are found.
Oracle Alerts are used to monitor unusual or critical activity within a designated database. The flexibility of ALERTS allows a database administrator the ability to monitor activities from table space sizing to activities associated with particular applications. Alerts can be created to monitor a process in the database and to notify a specific individual of the status of the process.
2. What are the different types of alerts, Define it?
You can define one of two types of alerts: an event alert or a periodic alert.
Event alert: An event alert immediately notifies you of activity in your database as it occurs.
Periodic alert: A periodic alert, on the other hand, checks the database for information according to a Schedule you define.
3. What are the different business uses of Alerts?
a) Keep you informed of critical activity in your database
b) Deliver key information from your applications, in the format you choose to provide you with regular reports on your database information
c) Automate system maintenance and routine online tasks Information about exception conditions.
4. What can be done with Alerts?
· You can send notifications
· You can send log files as attachments to notifications
· You can call PL/SQL stored procedures.
· You can send approval emails and get the results.
· Print some content dynamically
5. What types of actions can be generated when an Alert is triggered?
When an alert is executed, the alert can send an email message, run a concurrent program, run an operating system script, or run a SQL statement script. Using response processing, Oracle Alerts can solicit a response from a specific individual and perform an action based on the response that it receives.
6. What is On-Demand periodic alert?
It is a periodic alert with frequency as ‘On-Demand’. That means there is no specific period assigned to this alert and you can run this alert at any time you want using Request Periodic Alert Check form.
7. What database events can cause what actions?
An insert and/or an update to a specific database table
8. What actions can you perform in an alert?
An action can entail sending someone an electronic mail message, running a concurrent program, running an operating script, or running a SQL statement script. You include all the actions you want Oracle Alert to perform, in an action set.
9. How event alert works?
When you define an event alert to monitor a table for inserts and/or updates, any insert or update to the table will trigger the event alert. When an insert or update to an event table occurs, Oracle Alert submits to the concurrent manager, a request to run a concurrent program called Check Event Alert. The concurrent manager runs this request according to its priority in the concurrent queue. When the request is run, Check Event Alert executes the alert Select statement. If the Select statement finds exceptions, Check Event Alert performs the actions defined in the enabled action set for the alert. If the Select statement does not find any exceptions, Check Event Alert performs the No Exception actions in the enabled action set for the alert.
10. What do you specify when creating a Periodic Alert?
a. A SQL Select statement that retrieves specific database information
b. The frequency that you want the periodic alert to run the SQL statement
c. Actions that you want Oracle Alert to perform once it runs the SQL statement.
11. Can you define Alert on Oracle Applications Tables?
Yes
12. What is Periodic Set?
You can create a set of periodic alerts that Oracle Alert checks simultaneously. Use the Request Periodic Alert Check window to check the periodic set. Note that each periodic alert you include in a periodic set continues to run according to its individually defined frequency.
13. How alert is different from database triggers?
a) Code can be modified and viewed in a screen
b) Periodic alert is not possible through Database trigger
c) Oracle Alert will also transfer your entire alert definition across databases. You can instantly leverage the work done in one area to all your systems.
d) Customizable Alert Frequency with Oracle Alert, you can choose the frequencyof each periodic alert. You may want to check some alerts every day, some only once a month, still others only when you explicitly request them.
14. What is Action Set?
An action set can include an unlimited number of actions and any combination of actions and action groups for your alert. You can define as many action sets as you want for each alert. Oracle Alert executes the alert Select statement once for each action set you define. During each action set check, Oracle Alert executes each action set member in the sequence you specify.
15. Can you define detailed or summary actions in alert?
Yes, Detail or Summary Actions you can choose to have Oracle Alert perform actions based on a single exception or a combination of exceptions found in your database.
16. What is Distribution List in Oracle Alert?
Distribution lists let you predefine a set of message recipients for use on many actions. If a recipient changes, you need only adjust it in the distribution list, not in the individual message actions.
17. Can you specify History Maintenance?
Alert History Oracle Alert can keep a record of the actions it takes and the exceptions it finds in your database, for as many days as you specify.
18. Can you perform actions when NO exceptions are found?
No Exception Actions : Oracle Alert can perform actions if it finds no exceptions in your database, same as alert actions.
19. What are the Action Levels for your alert actions?
There are three types of level for your action: Detail, Summary and No Exception.
During an alert check, a detail action performs once for each individual exception found, a summary action performs once for all exceptions found, and a no exception action performs when no exceptions are found.
No comments:
Post a Comment